今回は、乳がん患者に対して多職種による集学的体重管理を行った効果について調査した研究を紹介します。
今まで、特に乳がん患者さんに対する体重管理の重要性について紹介してきました。
リンパ浮腫の予防のためにも体重管理は重要でしたね。
しかし、化学療法の副作用も相まって、体重増加しやすいことも少なくありません。
痛みに関しては、集学的アプローチといって、多職種で連携して痛みに対する治療を行うことも多くなっています。
体重管理も多職種で行うと効果が出そうな気はしませんか?
そこで、今回は乳がん患者に対して多職種による集学的体重管理を行った効果について調査した研究を紹介します。
・集学的な体重管理は、体重増加を最小限に抑え、体格構成を改善することにより、早期乳がんの生存にプラスの役割を果たすと思われる。
・メタボになる前に、集学的体重管理を行うことはよりよい効果が期待できる。
・自分で自己管理が難しい場合には、医療者による集学的管理を行ってもらうことが効果的と思われるが、日本では対応できる施設が少ないことが課題である。
今回紹介する研究の概要
今回紹介する論文は、乳がん患者に対して多職種による集学的体重管理を行った効果について調査した内容になっています。
「Nguyen V, Chen J, Lord R, et al. The Impact of Multidisciplinary Weight Management on Body Weight and Body Mass Composition in Women with Breast Cancer Post-Adjuvant Chemotherapy: A Retrospective Chart Review. Oncology. 2022 Apr 11.」、2022年に発行された最新の論文です。
女性のためのソイプロテイン ジェシカズ・フォーミュラ対象
Retrospective data were obtained from women undergoing multidisciplinary weight management at the Macquarie University (MQ) Health Healthy Weight Clinic (HWC), based in Sydney, Australia, between 28th July 2017 to 19th July 2021. The MQ Health HWC consists of a team of endocrinologists, dietitians and exercise physiologists that coordinate an individualised plan of weight management on a dietary, medical and physical activity level. From the clinic, women with breast cancer who had received adjuvant chemotherapy, and women without cancer were recruited into the study via convenience sampling. 414 women were identified as HWC patients, with 341 participants being excluded after inclusion and exclusion criterion were applied, with an additional 41 participants being excluded due to missing follow-up data. The remaining number of participants included in the study were 11 women in the breast cancer cohort, and 21 women in the control cohort. All study participants had to be at least 18 years old. Women with primary Stage I-IIIB breast cancer who had received adjuvant chemotherapy were eligible for the study. Exclusion criteria for both groups included medical conditions or medications that may affect weight loss, such as Cushing’s Syndrome, untreated thyroid disease, severe cardiorespiratory disease, movement limiting arthritis, anti-depressants, corticosteroids and sulfonylureas, and history of other cancers. Women with breast cancer who had had recurrent disease, distant metastases or no chemotherapy were also excluded.
Nguyen V, Chen J, Lord R, et al. The Impact of Multidisciplinary Weight Management on Body Weight and Body Mass Composition in Women with Breast Cancer Post-Adjuvant Chemotherapy: A Retrospective Chart Review. Oncology. 2022 Apr 11.
対象は、2017年7月28日から2021年7月19日の間に、オーストラリア・シドニーに拠点を置くマッコーリー大学(MQ)健康体重クリニック(HWC)で集学的体重管理を受けた女性で、乳がんコホートの女性11人、対照コホートの女性21人でした。
研究参加者は全員、18歳以上であることが条件とされました。
アジュバント化学療法を受けたI-IIIB期の乳がん患者が対象とされています。
両群の除外基準には、クッシング症候群、未治療の甲状腺疾患、重度の心肺疾患、運動を制限する関節炎、抗うつ薬、コルチコステロイド、スルホニル尿素などの体重減少に影響を及ぼす可能性のある病状や薬剤、他の癌の既往などが含まれていました。また、再発した乳がん、遠隔転移した乳がん、化学療法を受けなかった乳がん女性も除外されました。
女性のためのソイプロテイン ジェシカズ・フォーミュラ方法
Demographic and clinical characteristics Demographic information, age, smoking status, menopausal status, MetS status and past medical history was obtained from the patient’s HWC EMR, pathology orders, reports and referral letters. MetS status was determined using the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel III (ATP III) criteria, due its clinical and epidemiological application.Body weight and mass composition BMI was calculated from weight measures taken on bariatric digital weighing scales in the clinic, and baseline height was taken using a calibrated stadiometer, to ensure consistent measurements.
Nguyen V, Chen J, Lord R, et al. The Impact of Multidisciplinary Weight Management on Body Weight and Body Mass Composition in Women with Breast Cancer Post-Adjuvant Chemotherapy: A Retrospective Chart Review. Oncology. 2022 Apr 11.
基本情報として年齢、メタボリックシンドローム(Mets)喫煙状況、閉経状況、過去の病歴、腫瘍の病期、グレード、特徴および治療に関する情報を調査しています。
体重および質量組成 BMIは、診療所の肥満用デジタル体重計で測定した体重から算出ています。
女性のためのソイプロテイン ジェシカズ・フォーミュラ結果
Nguyen V, Chen J, Lord R, et al. The Impact of Multidisciplinary Weight Management on Body Weight and Body Mass Composition in Women with Breast Cancer Post-Adjuvant Chemotherapy: A Retrospective Chart Review. Oncology. 2022 Apr 11.
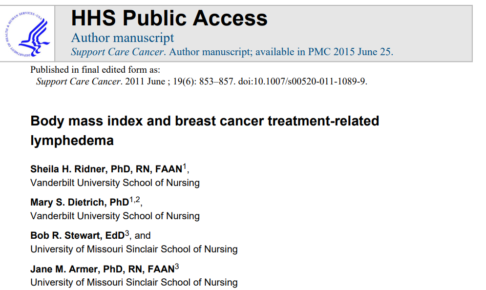
集学的体重管理のベースラインでは、対照コホートの平均体重は乳がんコホートより高かったが(p = 045)、ベースラインの体重差を調整した後の3ヵ月および6ヵ月では、両コホート間に全体的な有意差はありませんでした。
また、BMI、骨格筋量、脂肪量、ウエスト周囲径の平均値についても、ベースライン時の体重差で調整すると、すべての時間間隔で2つのコホート間に差は見られませんでした。
Nguyen V, Chen J, Lord R, et al. The Impact of Multidisciplinary Weight Management on Body Weight and Body Mass Composition in Women with Breast Cancer Post-Adjuvant Chemotherapy: A Retrospective Chart Review. Oncology. 2022 Apr 11.
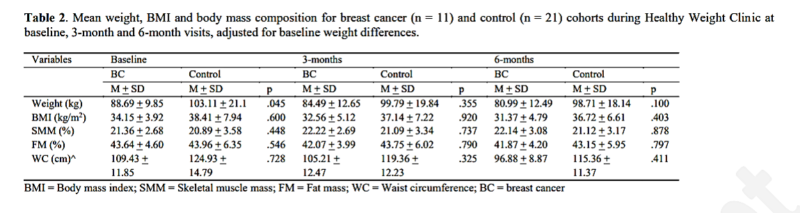
乳がんコホートについては、6ヵ月後までの乳がん女性の平均体重変化は-6.99 + 3.87kg(p = .003)、BMI変化は-2.72 + 1.62 kg/m2(p = .004)で、体重変化は-8.13%に相当していました。
骨格筋量は1.21+0.73%(p=0.005)、脂肪量は-2.76+1.33%(p=0.002)、ウエスト周囲径は-8.13+4.21cm(p=0.031)でした。]
Nguyen V, Chen J, Lord R, et al. The Impact of Multidisciplinary Weight Management on Body Weight and Body Mass Composition in Women with Breast Cancer Post-Adjuvant Chemotherapy: A Retrospective Chart Review. Oncology. 2022 Apr 11.
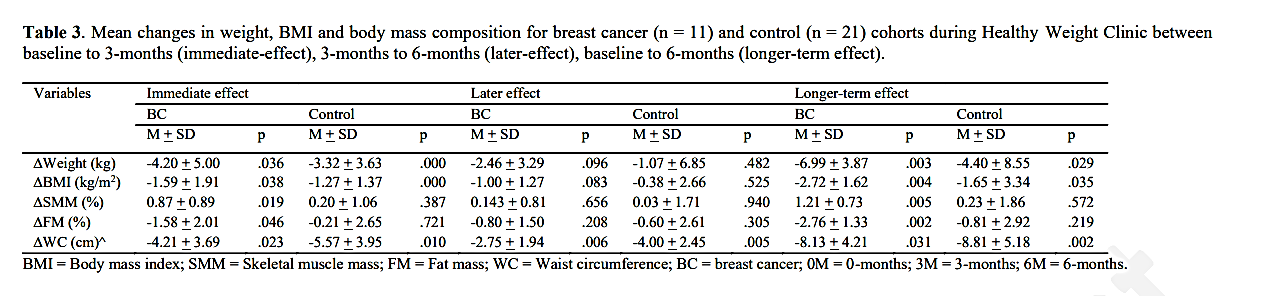
乳がんコホートでは、体重と体格構成は民族、喫煙状況、閉経状況によって有意な影響を受けなかったが、体重はMetSの有無によって有意な影響を受けていました。
6ヵ月後までに、MetSのある参加者(-2.65 + 3.75kg)に比べ、MetSのない参加者(-8.72 + 2.41kg)では体重に大きな変化がありました(p = 0.045)。
これはBMIの変化にも反映されていました(p = 0.039)が、MetSの状態による骨格筋量、脂肪量、ウエスト周囲径には変化がありませんでした(表4)。
対照コホートでは、民族、閉経状態、MetS状態による体重、BMI、骨格筋量、脂肪量、ウエスト周囲径に差はありませんでした。対照群には喫煙者がいなかったので、喫煙の有無は分析できませんでした。
女性のためのソイプロテイン ジェシカズ・フォーミュラ結論
Multidisciplinary weight management improves body weight and body mass composition in breast cancer women undergoing adjuvant chemotherapy. Although these findings are in a small sample size, it appears that multidisciplinary weight management has a positive role to play in early-stage breast cancer survival by minimising weight gain and improving body mass composition. Targeting pre-existing MetS status through lifestyle changes is also an important consideration, beyond a specific weight focus.
Nguyen V, Chen J, Lord R, et al. The Impact of Multidisciplinary Weight Management on Body Weight and Body Mass Composition in Women with Breast Cancer Post-Adjuvant Chemotherapy: A Retrospective Chart Review. Oncology. 2022 Apr 11.
集学的な体重管理は、アジュバント化学療法を受けている乳がん女性の体重と体格構成を改善することがあきらかとなった。
これらの知見はサンプルサイズが小さいが、集学的な体重管理は、体重増加を最小限に抑え、体格構成を改善することにより、早期乳癌の生存にプラスの役割を果たすと思われます。
また、特定の体重に焦点を当てるだけでなく、ライフスタイルの変化を通じて既存のMetS状態をターゲットにすることも重要な検討事項となります。
詳しい指導内容が記載されていませんが、多職種での学際的な体重管理は、乳がん患者さんにとって効果がありそうな結果となっています。
特にメタボにまで陥ってない患者さんには、効果があるような結果ですね。
メタボになってしまう前に早めに自分で体重管理し、それでも無理ならば医療従事者に相談して管理してもらうことも一つの手段と思います。
ただし、日本ではなかなか病院で体重管理まで徹底してくれる施設は少ないのが課題ですね。
女性のためのソイプロテイン ジェシカズ・フォーミュラ・集学的な体重管理は、体重増加を最小限に抑え、体格構成を改善することにより、早期乳がんの生存にプラスの役割を果たすと思われる。
・メタボになる前に、集学的体重管理を行うことはよりよい効果が期待できる。
・自分で自己管理が難しい場合には、医療者による集学的管理を行ってもらうことが効果的と思われるが、日本では対応できる施設が少ないことが課題である。
このブログは、ガイドラインや論文などの根拠をもとに情報を発信していく予定です。
しかし、がんの病態や治療方法によっては、お読みになっているがん患者さんにはその情報が当てはまらない場合もあります。
記事の内容を参考に新しく何かを始める場合には、担当の医師や医療従事者にご確認いただくようお願いいたします。





















最近のコメント